44 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a Treasury bill? T-bills are also called as zero coupon bond, which is issued at discount. T bills are short term instruments issued within one year. 91 days, 182 days, 364 days are the examples of maturity period. T-bills are issued by goverment of any country. One point to remember US Treasury Bonds - Fidelity The coupon rate is fixed at the time of issuance and is paid every six months. Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity.
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due.
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
Joint Statement by Secretary of the Treasury Janet L. Yellen and Japan ... TOKYO — Ahead of the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors Meeting in Bali, Indonesia, Secretary of the Treasury Janet L. Yellen and Japan Finance Minister and Minister of State for Financial Services Suzuki Shunichi held an in-person bilateral meeting in Tokyo. Following the meeting, they issued the following joint-statement agreeing to further strengthen the U.S. and Japan's ... B treasury bills are zero coupon bonds c zero coupon B) Treasury bills are zero -coupon bonds. C) Zero -coupon bonds always trade at a discount. D) The yield to maturity is typically stated as an annual rate by multiplying the calculated YTM by the number of coupon payment per year, thereby converting it to an APR. Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia Examples of zero-coupon bonds include US Treasury bills, US savings bonds, long-term zero-coupon bonds, and any type of coupon bond that has been stripped of its coupons. Zero coupon and deep discount bonds are terms that are used interchangeably.
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) - Meaning, Examples, Calculations Treasury bills are a type of zero-coupon security where the central government borrows funds from the individual for a period of 364 days or less. In return, the investors receive interest. These money market instruments provide a return on investment at once, and there is no provision for periodic returns. Treasury Bonds | CBK Jun 13, 2022 · five year and fifteen year fixed coupon treasury bonds issue nos. fxd 1/2013/5 & fxd 2/2013/15: 25/03/2013: two year and re-opening of ten year fixed coupon treasury bonds issue nos. fxd 2/2013/2 & fxd 1/2012/10: 25/02/2013: two and fifteen year fixed coupon treasury bonds issue nos. fxd 1/2013/2 & fxd 1/2013/15: 09/01/2013 Institutional - The Basics of Treasury Securities How do Treasury bills, notes, bonds, FRNs, and TIPS differ from savings bonds? Unlike savings bonds, Treasury bills, notes, bonds, FRNs, and TIPS are transferable, so you can buy or sell them in the securities market. You can buy Treasury bills, notes, bonds, FRNs, and TIPS for a minimum of $100, and you can buy savings bonds for as little as $25. Treasury Bills - Guide to Understanding How T-Bills Work Treasury Bills (or T-Bills for short) are a short-term financial instrument issued by the US Treasury with maturity periods from a few days up to 52 weeks. ... They have a maturity period of between 20 years and 30 years, with coupon payments every six months. T-bond offerings were suspended for four years between February 2002 and February ...
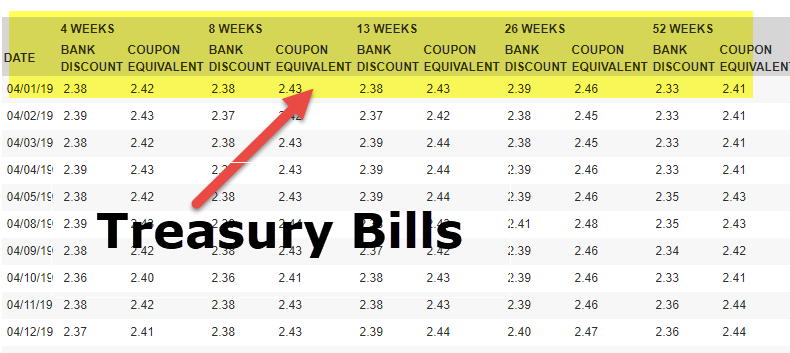
Treasury Bills - Meaning, Types, Yield Calculation & How to Buy? Sep 10, 2020 · Treasury bills are zero-coupon bonds, i.e. no interest is paid on them to investors. They are issued at a discount and redeemed at face value. Therefore, the returns earned by investors in T-bills remains fixed throughout the bond tenure irrespective of the economic condition of the country. Frequently Asked Questions - U.S. Department of the Treasury The par yield curve is based on securities that pay interest on a semiannual basis and the yields are "bond-equivalent" yields. Treasury does not create or publish daily zero-coupon curve rates. Does the par yield curve only assume semiannual interest payment from 2-years out (i.e., since that is the shortest maturity coupon Treasury issue)? No. A guide to US Treasuries Treasuries are issued in six main structures. Usually, the longer the maturity, the higher the interest rate, or coupon.. Treasury bills (T-bills): T-bills have the shortest maturities at four, eight, 13, 26, and 52 weeks. T-bills are typically issued at a discount to par (or face) value, with interest as well as principal paid at maturity. What is Treasury Bill (T-bill)? - Indian Economy Treasury bills are presently issued in three maturities, namely, 91 day, 182 day and 364 day. Treasury bills are zero coupon securities and pay no interest. Rather, they are issued at a discount (at a reduced amount) and redeemed (given back money) at the face value at maturity.
14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting This zero-coupon bond was sold for $2,200 below face value to provide interest to the buyer. Payment will be made in two years. The straight-line method simply recognizes interest of $1,100 per year ($2,200/2 years). Figure 14.11 December 31, Years One and Two—Interest on Zero-Coupon Bond at 6 Percent Rate—Straight-Line Method Treasury Bonds vs. Treasury Notes vs. Treasury Bills Mar 29, 2022 · Note Auction: A formal bidding process that is scheduled on a regular basis by the U.S. Treasury. Currently there are 17 authorized securities dealers (primary dealers) that are obligated to bid ... Treasury Bills - Types, Features and Advantages of Government ... - Groww Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities, issued at a discount to investors. Hence, total returns generated by such instruments remain constant through the tenure of bond, irrespective of economic conditions and business cycle fluctuations. Individual - Treasury Bonds: Rates & Terms Treasury Bonds: Rates & Terms Treasury bonds are issued in terms of 20 years and 30 years and are offered in multiples of $100. Price and Interest The price and interest rate of a bond are determined at auction. The price may be greater than, less than, or equal to the bond's par amount (or face value). (See rates in recent auctions .)
Zero Coupon Bond Funds: What Are They? - The Balance A zero coupon bond is a bond that doesn't offer interest payments but sells at a discount—a price lower than its face value. 1 The bondholder doesn't get paid while they own the bond, but when the bond matures, they will be repaid the full face value. Zero coupon bond funds are funds that hold these types of bonds.
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1 Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: Issued at deep discount and redeemed at full face value
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula It is also called a pure discount bond or deep discount bond. U.S. Treasury bills are an example of a zero-coupon bond. Summary A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds.
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Definition - Investopedia T-bills are zero-coupon bonds that are usually sold at a discount and the difference between the purchase price and the par amount is your accrued interest. How Can I Buy a Treasury Bill? U.S....
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) Bonds are debt instruments also issued by the government or corporate for tenure equal to or more than 2 years period. T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment.
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000.
why is treasury bill also called as zero coupon bonds - Brainly.in Treasury notes also referred to as Zero-Coupon Bonds. • They are available for a minimum of and in multiples of that amount. • A treasury bill is a short-term borrowing instrument used by the Indian government that has a maturity of less than a year. • Treasury bills, which are sold to banks and the general public, allow the government to ...
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds Jan 31, 2022 · Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds have a poor risk-return profile when held alone. Long-dated zero-coupon Treasury bonds are more volatile than the stock market, but they offer the lower long-run ...
Government - Continued Treasury Zero Coupon Spot Rates* 3.20. 3.38. 3.79. *Four quarters covering calendar year 2012 and the first and second quarters of calendar year 2013 prepared by Economic Policy (EP) using the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) legacy model. Legacy model quarterly rates can be viewed within the "Selected Asset and Liability Price Report" under "Spot (Zero ...
Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Excel Calculator - Wall Street Prep U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000.
Investing in Treasury Bills: The Safest Investment in 2022? Most bonds are usually issued with a face value of $100 or $1,000. By comparing the present value of the T-bill to its face value, an investor knows whether the bond is overvalued or undervalued. Coupon — The coupon states how much interest the bond will pay. Bonds usually pay this interest semi-annually.
United States Treasury security - Wikipedia Treasury bills (T-bills) are zero-coupon bonds that mature in one year or less. They are bought at a discount of the par value and, instead of paying a coupon interest, are eventually redeemed at that par value to create a positive yield to maturity.. Regular weekly T-bills are commonly issued with maturity dates of 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 13 weeks, 26 weeks, and 52 weeks.
Treasury Coupon Issues | U.S. Department of the Treasury Treasury Coupon Issues The Yield Curve for Treasury Nominal Coupon Issues (TNC yield curve) is derived from Treasury nominal notes and bonds. The Yield Curve for Treasury Real Coupon Issues (TRC yield curve) is derived from Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS).
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Best Differences (With ... Let us Discussed some of the major differences between Treasury Bills vs Bonds: Treasury bills are short term money market instruments whereas Treasury Bonds are long term capital market instruments. Treasury bills are issued at a discounted price whereas Treasury Bonds pay interest every six months to holders of a bond. Treasury bills mature ...
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia Examples of zero-coupon bonds include US Treasury bills, US savings bonds, long-term zero-coupon bonds, and any type of coupon bond that has been stripped of its coupons. Zero coupon and deep discount bonds are terms that are used interchangeably.
B treasury bills are zero coupon bonds c zero coupon B) Treasury bills are zero -coupon bonds. C) Zero -coupon bonds always trade at a discount. D) The yield to maturity is typically stated as an annual rate by multiplying the calculated YTM by the number of coupon payment per year, thereby converting it to an APR.
Joint Statement by Secretary of the Treasury Janet L. Yellen and Japan ... TOKYO — Ahead of the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors Meeting in Bali, Indonesia, Secretary of the Treasury Janet L. Yellen and Japan Finance Minister and Minister of State for Financial Services Suzuki Shunichi held an in-person bilateral meeting in Tokyo. Following the meeting, they issued the following joint-statement agreeing to further strengthen the U.S. and Japan's ...














Post a Comment for "44 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds"